When and why does heating water need to be treated?
- why the requirements exist
- possible damages and their backgrounds
- overview of quality parameters
- methods of treatments
Heating water is not just water that you can take from the tap. For the proper operation of your system, there are certain requirements for the quality of the water. These requirements are regulated in VDI 2035 – Prevention of damage in hot water heating systems. If these requirements are not met, the manufacturer’s warranty may be voided and damage may occur. To prevent this, your heating water should be checked and possibly treated every time it is filled. In today’s article we will explain what you have to pay attention to.
Why the requirements exist
The heating water should transfer the heat from the boiler to the radiator without a high energy loss. To ensure that this process runs smoothly, the water must have a certain composition. Your heating system most likely consists of different materials such as metals and plastics that have different chemical properties. So that these do not react with the water is to be considered some things. For example, particularly hard water can lead to the formation of stones. Too high electrical conductivity can cause corrosion of the various metals.
Why the requirements exist
The heating water should transfer the heat from the boiler to the radiator without a high energy loss. To ensure that this process runs smoothly, the water must have a certain composition. Your heating system most likely consists of different materials such as metals and plastics that have different chemical properties. So that these do not react with the water is to be considered some things. For example, particularly hard water can lead to the formation of stones. Too high electrical conductivity can cause corrosion of the various metals.
Quality parameters
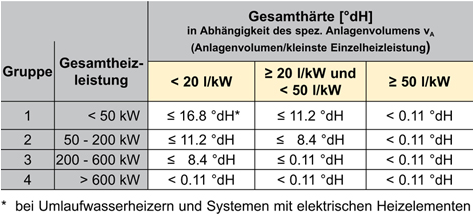
Water hardness
Water is particularly hard if there are too many calcium and magnesium ions in the heat transfer medium. If the value is too high, stone formation is favored.
pH value
This value provides information about the acidity of the water. Since substances such as aluminum are sensitive to low pH values, corrosion can occur.
Conductivity
If there are a lot of metals in the water, the electrical conductivity is higher. These metals promote both corrosion and the formation of stones.
Methods of treatment
The VDI 2035 gives 4 different methods, each with different objectives, to choose from. Which method to use depends on factors such as the quality of the drinking water and the condition of your heating system. The expert can decide on the basis of these factors and the guideline values of the VDI 2035 which procedure is the best for you.
Softening
Calcium and magnesium ions are exchanged for sodium ions, which pose a much lower risk of stone formation. However, electrical conductivity and pH remain unchanged.
Demineralization
Demineralization removes any minerals and salts from the water. In the process, electrical conductivity is lowered, which prevents corrosion caused by electrolysis. However, it should be noted that completely desalinated water, comparable to a sponge, sucks salts and minerals out of the components. This nullifies the desired effect. The pH value is also changed by desalination. Inhibitors are used to counteract these effects.
Conclusion
The treatment of heating water is necessary to prevent damage caused by corrosion and stone formation. The quality of the drinking water and the condition of the system are crucial factors in determining the necessary measures. The filling of a system, whether during installation or maintenance, is the right time to check the values specified in VDI 2035 and, if necessary, to carry out treatment.


